02 Jul Analysis of Positional Areas and Match Outcomes in the 2023/24 LALIGA EA Sports Season
Abstract
This study investigates the relationship between the area occupied by football teams during offensive and defensive phases and their match outcomes in the 2023/24 LALIGA EA Sports season. Our analysis reveals that teams with a larger area in the offensive phase and a smaller area in the defensive phase have a statistically significant advantage in winning matches. The findings offer practical implications for coaching strategies focused on spatial management.
Introduction
The area a football team occupies on the field, both when in possession of the ball (offensive phase) and without the ball (defensive phase), can significantly impact match outcomes. This study explores the correlation between these positional areas and the success rate of teams in the 2023/24 LALIGA EA Sports season, providing valuable insights for optimizing team performance.
Methodology
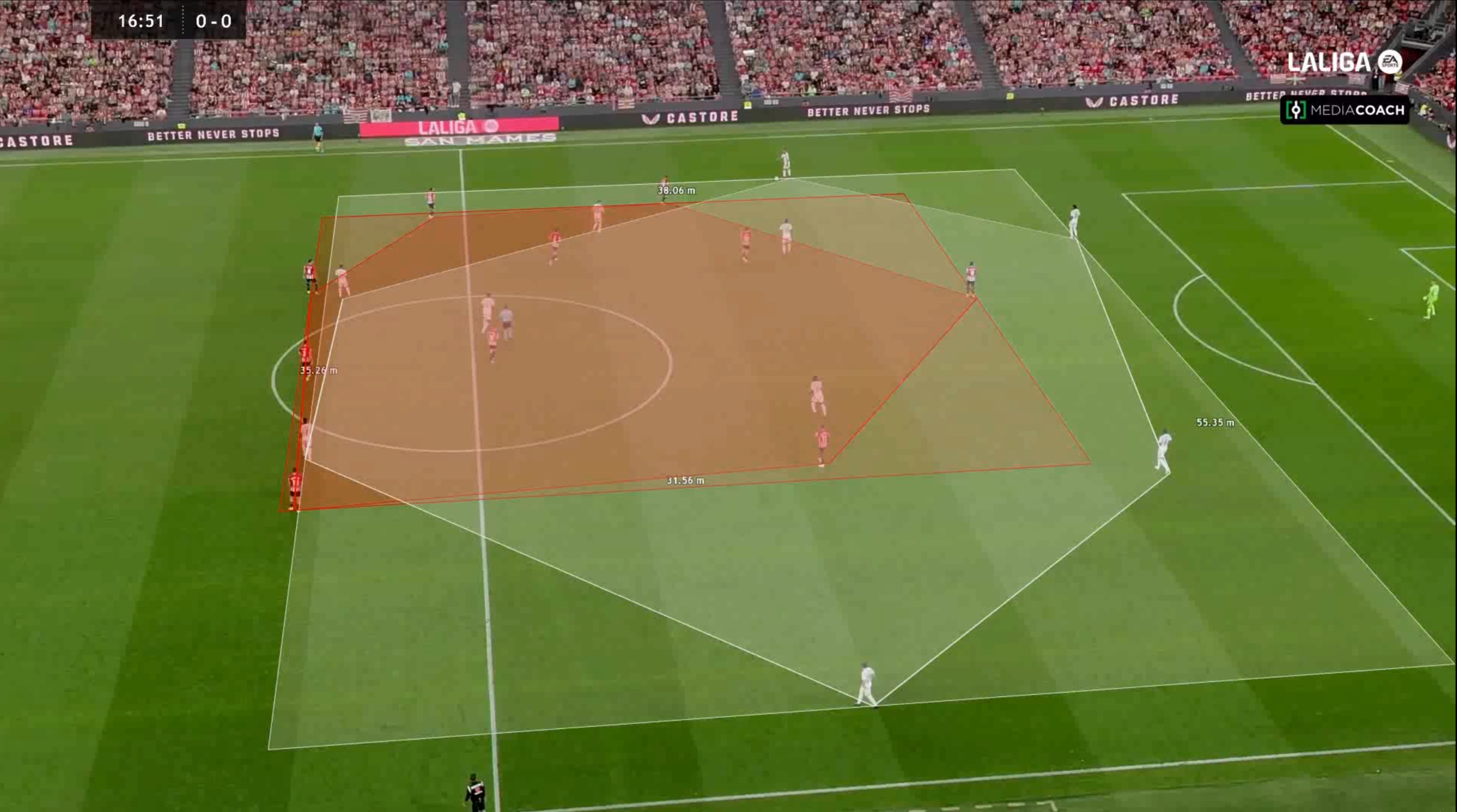
Data were collected from all matches in the 2023/24 LaLiga EA Sports season. Each team’s positional area was calculated during offensive and defensive phases using the product of the depth and width occupied on the field. The analysis focused on two main hypotheses:
- Teams with a larger offensive area and a smaller defensive area are more likely to win matches.
- There is a significant correlation between offensive area and goals scored, and defensive area and goals conceded.
Results
Combined Analysis
Teams with a larger offensive area and a smaller defensive area won 65.2% of their matches. This finding was statistically significant with a p-value of 0.0027, indicating a strong correlation between this spatial strategy and match success.
Separate Analysis
- Offensive Area and Goals Scored:
- Teams with a larger offensive area scored more goals than their rivals in a significant proportion of matches. The p-value of 0.0015 confirms the statistical significance of this relationship.
- Defensive Area and Goals Conceded:
- Teams with a smaller defensive area conceded fewer goals than their rivals. This relationship was also statistically significant, with a p-value of 0.0055.
Discussion
The results of this study highlight the importance of spatial management in football. Teams that effectively expand their area during the offensive phase and compact their area during the defensive phase have a higher probability of winning matches. These findings can inform coaching strategies aimed at optimizing team performance through better spatial utilization.
Case Studies
- GIRONA FC: Led the league in offensive area with an average of 1764.37 m² and achieved notable success in their match outcomes.
- FC BARCELONA: Demonstrated a balanced approach with a large offensive area and a compact defensive area, contributing to their competitive performance.
Practical Implications for Coaches
Based on the findings, coaches are advised to:
- Encourage Expansion: Train teams to utilize the full width and depth of the field during the offensive phase to disrupt the opponent’s defense.
- Promote Compaction: Instruct teams to compact their formation during the defensive phase, reducing spaces and making it difficult for opponents to create goal-scoring opportunities.
Conclusion
This study provides a quantitative perspective on the significance of the area occupied by football teams in both offensive and defensive phases. The findings underscore the importance of spatial management for achieving competitive success on the field. Future research could further explore these relationships across different leagues and competitive levels.


