06 Mar Advanced Model for Analyzing Defensive Line Depth: A LALIGA EA Sports 2024/25 Perspective
Introduction
One of the most critical moments in any football match is managing passes played behind the defensive line. This is especially risky for teams that defend with a high line, as these balls create constant threats that can determine the outcome of a game. To better understand this tactical scenario, LALIGA’s Football Intelligence & Performance Department has developed an advanced tactical camera video analysis model to extract insights that can be applied in both training and competition.
After analyzing data from LALIGA EA Sports teams during the 2024/25 season, we identified a key pattern: 9 out of 20 teams, when losing, push their defensive line at least 5% higher compared to their average positioning in matches they do not lose. This suggests that an aggressive defensive line might increase risk if not executed correctly. But what are the key elements that should be trained to manage this situation more effectively?
Tactical Insights from the Analysis
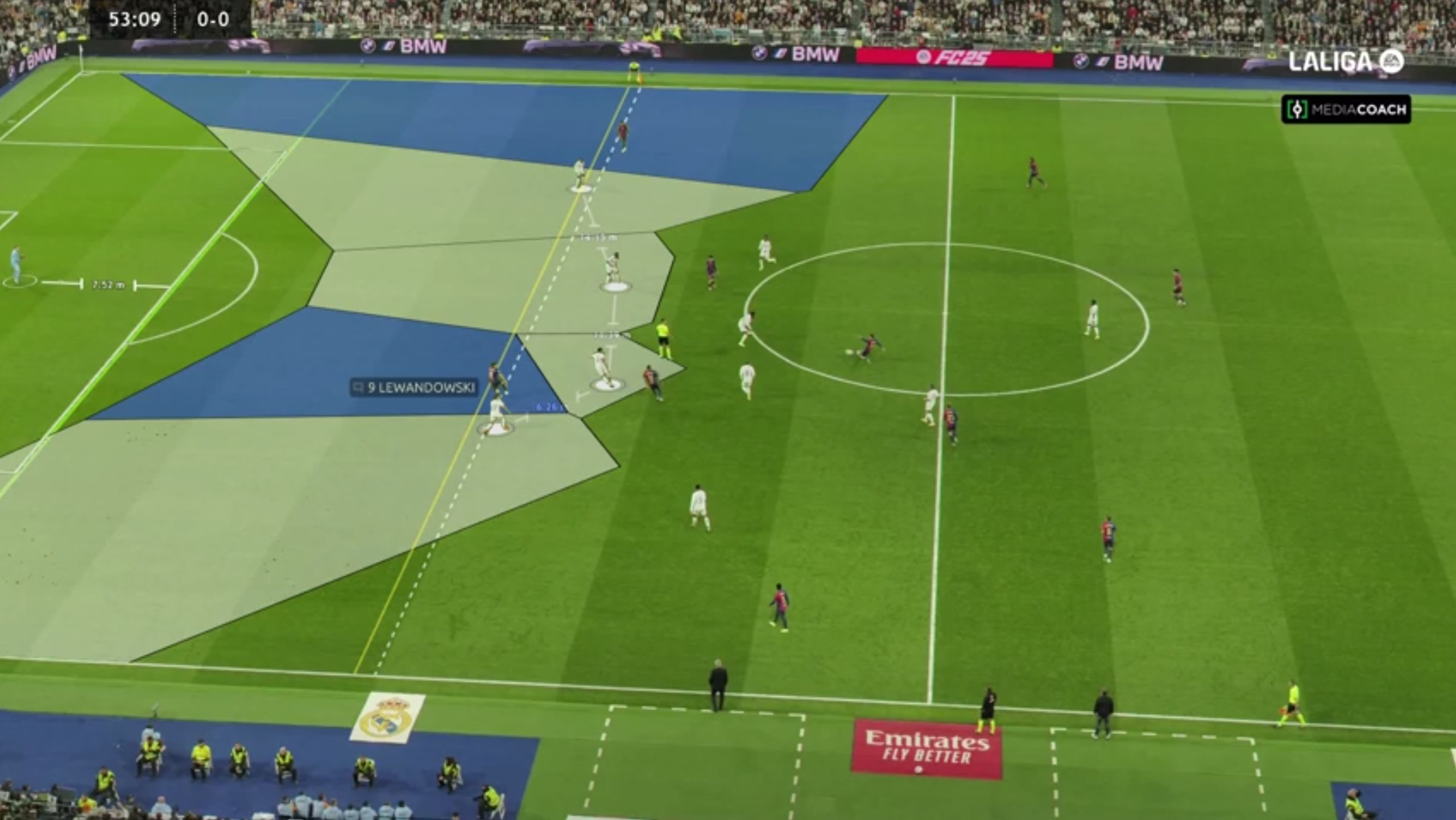
Our model does not only analyze defensive line positioning but introduces three fundamental aspects to better understand and defend against passes in behind:
1. The Offside Line as a Defensive Tool
- The position of the last defender determines the offside line.
- The model tracks the attacker closest to this line and marks the exact frame when the pass is played.
- If the attacker moves beyond the line before the pass is played, the graphical overlay turns red, signaling an offside position.
- Application in training: Defensive line coordination drills to ensure synchronization with pressing actions that force opponents into offside traps.
2. Space Control Using a Voronoi-Based Model
- The model visualizes the space occupied by the defensive line and nearby opposition attackers.
- This space is dynamic, adjusting according to each player’s maximum speed and acceleration.
- Faster attackers have larger influence zones, making them more dangerous in runs behind the defense.
- Application in training: Adjusting the height of the defensive line based on the speed of opposing forwards and defenders’ ability to recover.
3. The Goalkeeper’s Role in Defending Space Behind
- The goalkeeper’s positioning directly impacts the available space for opposing attackers.
- A high-positioned goalkeeper reduces the attacking space, cutting off long passes before they reach their target.
- The model also evaluates the goalkeeper’s acceleration and maximum speed, which are crucial in reacting to through balls.
- Application in training: Developing goalkeepers’ decision-making on when to step up and when to retreat, optimizing their ability to sweep behind the defense.
How to Apply These Findings in Competition
- Opponent Pre-Match Analysis: Understanding the speed of opposition forwards and their defensive line tendencies helps in tactical planning.
- Coordinated Defense-Goalkeeper Work: A goalkeeper with strong acceleration can allow the defensive line to play higher with reduced risk.
- Scenario-Specific Training Drills: Real-match simulations to improve defensive line synchronization and goalkeeper reactions to through passes.
Conclusions
This analysis confirms that teams struggling to manage their defensive line in defending through balls could be increasing their risk of conceding goals. The key is not just about pushing the line higher or deeper, but ensuring proper coordination with the goalkeeper, reading attackers’ movements, and adjusting positioning based on player acceleration and speed.
Coaches can integrate these insights into their weekly planning, ensuring their teams not only master the offside trap but also effectively control space and optimize goalkeeper interventions. By leveraging data-driven insights and tactical video overlays, teams can turn what is often a defensive weakness into a strategic advantage.


